Ronny Mees | Emerson Network Power

Today’s most innovative data centers are generally equipped with managed PDUs since their switching capabilities improve reliability. However, simply installing managed PDUs is not enough – an “unmanaged” managed PDU will actually reduce reliability.
So how do managed PDUs work? These advanced units offer a series of configurations which – if properly implemented – improve the availability of important services. The main features are Software Over Temperature Protection (SWOTP) and Software Over Current Protection (SWOCP), which are well described in the blog post “Considerations for a Highly Available Intelligent Rack PDU”.
It is also well-known, that managed PDUs can support commissioning or repairing workflows in data centers. The combination of well designed workflows and managed PDUs pushes the operational reliability to a higher level.
In high performance data centers, using clusters, another important point comes into play: clusters are complex hierarchical structures of server farms, which are able to run high performance virtual machines and fully automated workflows.
As described here or here, such clusters are managed by centralized software together with server hardware.
Over the last couple of years cluster solutions have been developed following strong and challenging availability goals, in order to avoid any situation, which make physical servers struggle within the cluster. However, there would still be the risk of applications and processes generating faults and errors and screwing-up the complete cluster, unless there was an automated control process – the good news is: there is.
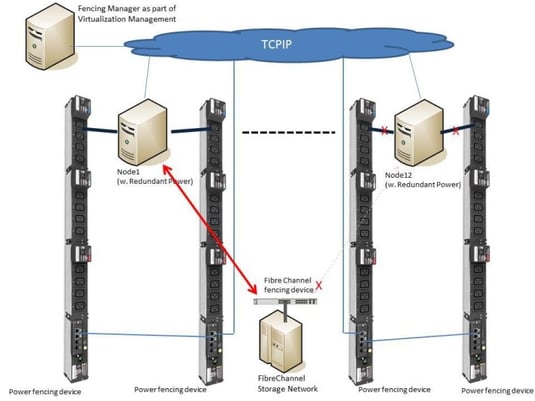
The process which controls those worst case scenarios is called fencing. Fencing automatically kicks out of the cluster any not working nodes or services in order to maintain the availability of the others.
Fencing has different levels, which are hopefully wisely managed. In a smooth scenario fencing will stop disturbing services, or re-organize storage access (Fibre channel switch fencing) to let the cluster proceed with its tasks.
Another power fencing option is also called “STONITH” (Shoot The Other Node In The Head) and allows the software to initiate an immediate shutdown (internal power fencing) of a node and/or a hard switch off (external power fencing).
The internal power fencing method uses IPMI and other service processer protocols, while the external power fencing uses any supported network protocol to switch of a PDU outlet. It is recommended to use secured protocols only, such as SNMPv3. So managed PDUs as MPH2 or MPX do not only support a nice power balance, monitor power consumptions or support datacenter operations workflows – they also allow the fence software to react quickly for higher cluster reliability. So it’s not a secret that cluster solutions manufacturers – e.g. Red Hat with RHEL 6.7 and newer – openly support such managed rack PDUs.
For More Emerson Network Power Blogs, Click Here